RNN Matrix Dimensions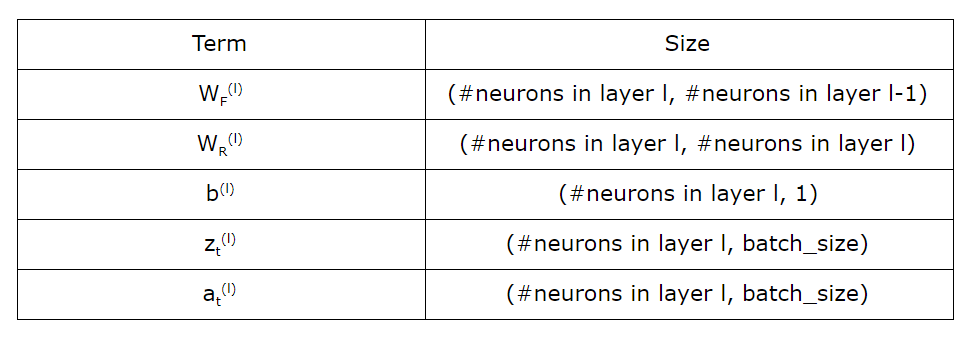 Many-to-Many RNN Architecture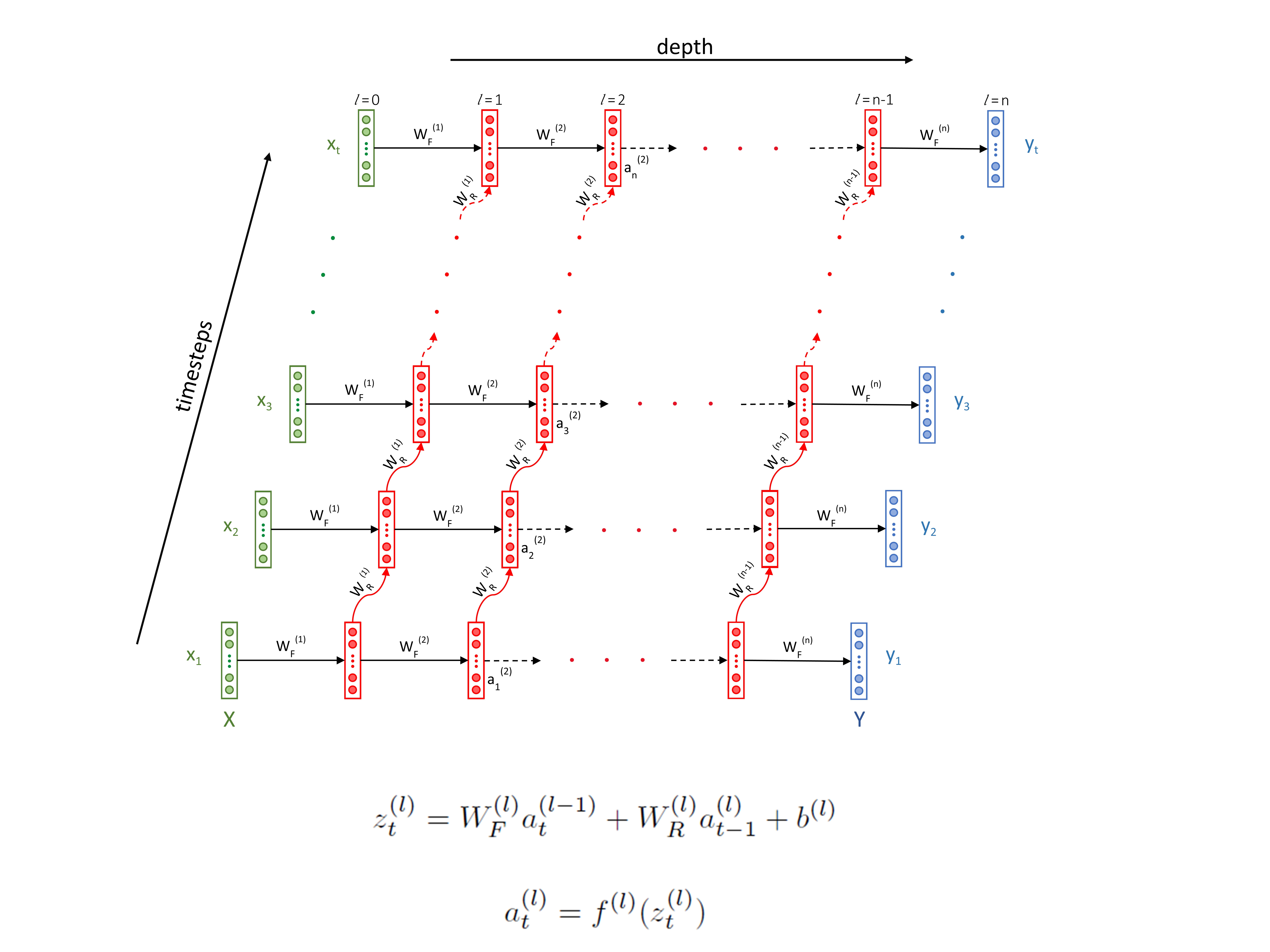 |
| RNN Architecture (Many-to-Many) |
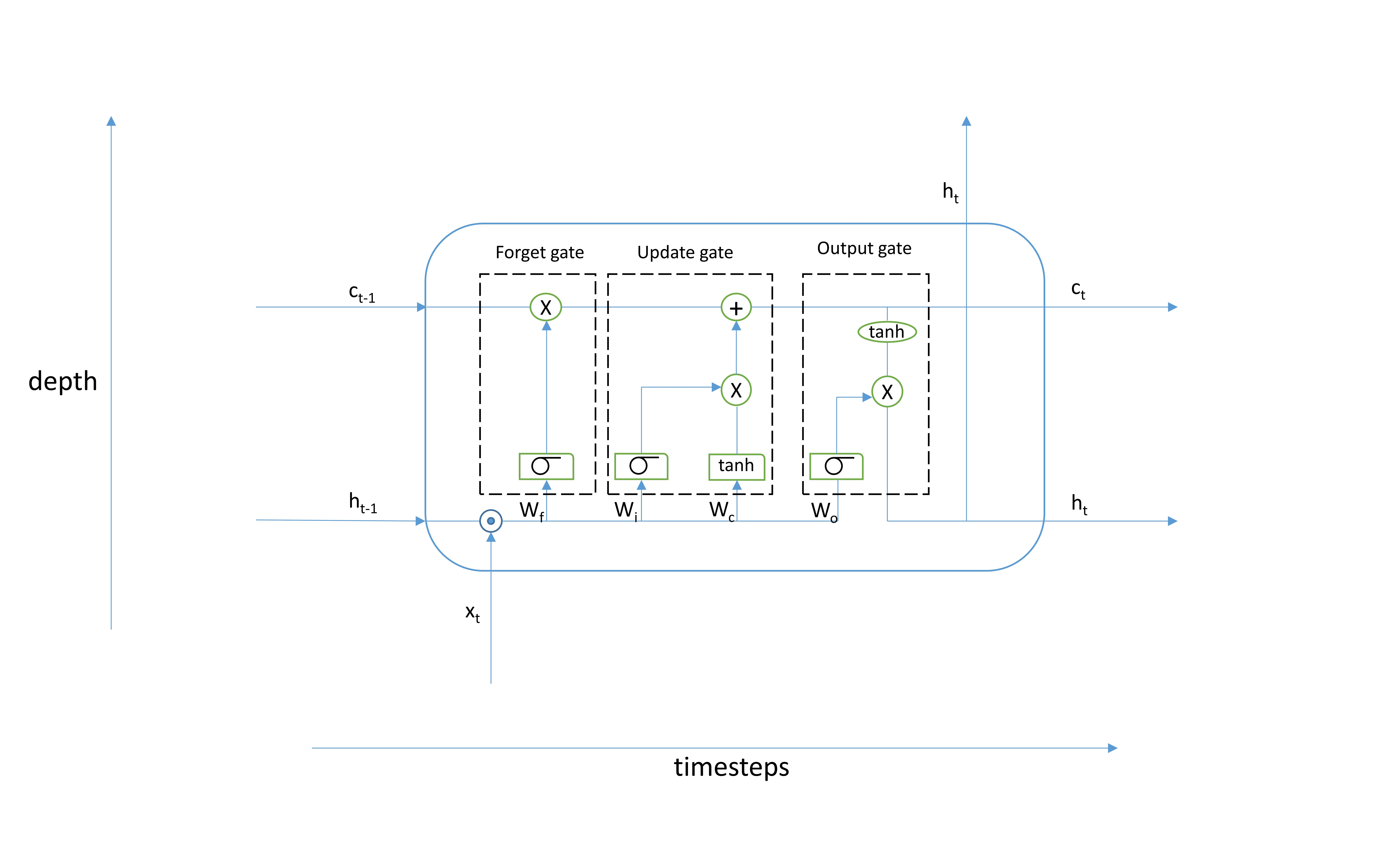
LSTM Cell Architecture (Long, Short-term Memory)
Key Components/Traits
- Cell State - a mechanism for memory
- Gating - a way to modify the cell state in certain ways. Main idea being regulating the information that the network stores (and passes on to the next layer) or forgets.
- Constant Error Carousel - A mechanism to bypass error to flow uninterrupted at a layer. Helps in arresting vanishing gradients.
In feedforward, first the previous activations and the current input get concatenated (shown by the dot operator). The concatenated vector goes into each of the three gates. The 'x' denotes element-wise multiplication while the '+' denotes element-wise addition between two vectors/matrices. Note that the output gate has another tanh function though it is not a gate (there are no weights involved in that operation, as shown in the figure).
The feedforward equations of an LSTM are as follows:
In the RNN cell, you had exactly one matrix (concatenation of the feedforward and the recurrent matrix). In case of an LSTM cell, you have four weight matrices:
Each of these is a concatenation of the feedforward and recurrent weight matrices. Thus, you can write the weights of an LSTM as:
-----------
No comments:
Post a Comment