CNN Architectures: Comparative Study
Source:
An Analysis of Deep Neural Network Models for Practical Applications
Comparison dimensions
- Number of model parameters
- Time taken for inference (essentially feed forward)
- Number of operations carried to do the inference
- Power consumption
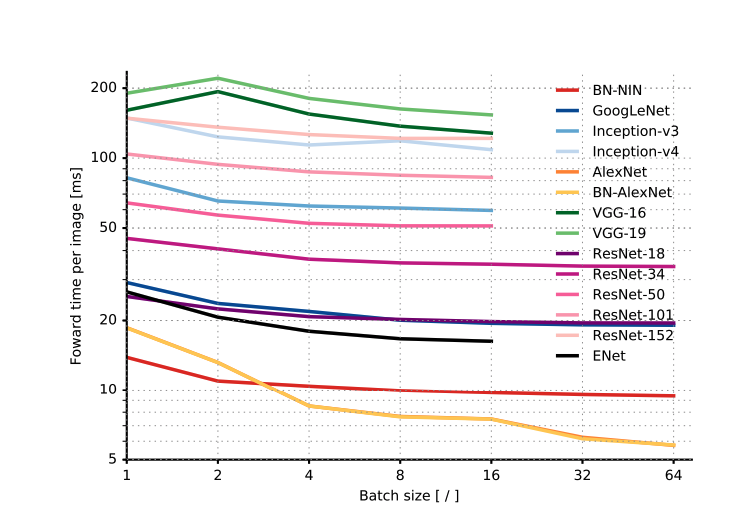
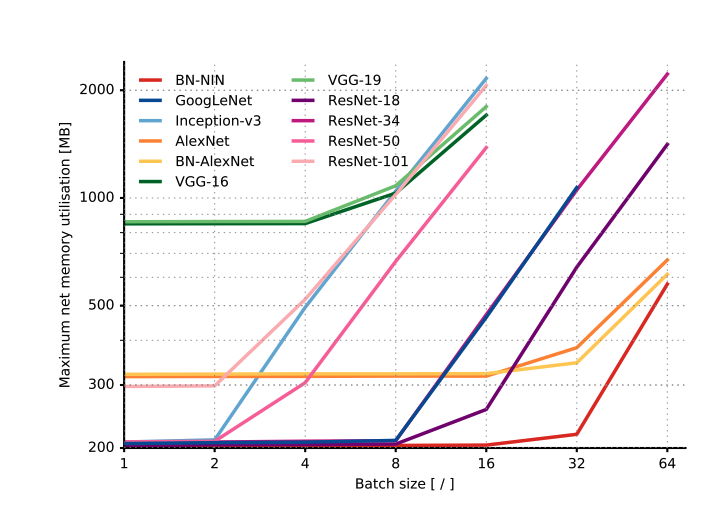
- Relationship with Batch size
Practical Application Considerations
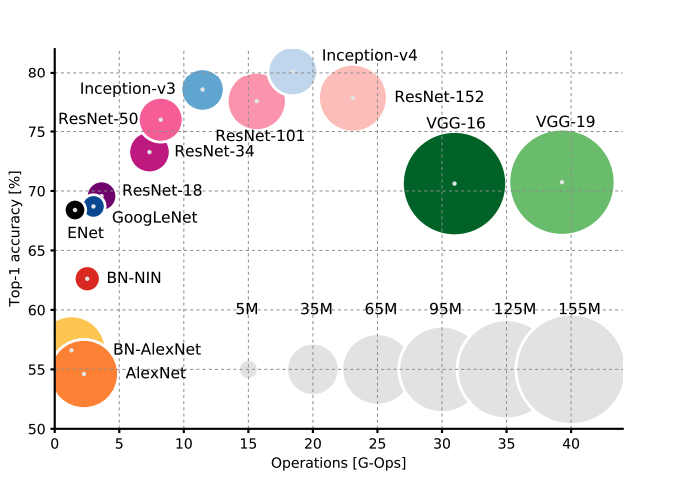
- Architectures in a particular cluster, such as GoogleNet, ResNet-18 and ENet, are very attractive since they have small footprints (both memory and time) as well as pretty good accuracies. Because of low-memory footprints, they can be used on mobile devices, and because the number of operations is small, they can also be used in real time inference.
- In some ResNet variants (ResNet-34,50,101,152) and Inception models (Inception-v3,v4), there is a trade-off between model accuracy and efficiency, i.e. the inference time and memory requirement.
- Most, if not all, models seem to have marginal improvement in time for inference as batch size is increased (except AlexNet)
- Power consumption for most models is around the same.
- Beyond a certain batch size, memory increases (shoots up) linearly with batch size. Until then, memory req is quite low. Thus, it might not be a bad idea to use a large batch size if you need to.
- Up to a certain batch size, most architectures use a constant memory, after which the consumption increases linearly with the batch size.
- Accuracy and inference time are in a hyperbolic relationship: a little increment in accuracy costs a lot of computational time
- Power consumption is independent of batch size and architecture.
- The number of operations in a network model can effectively estimate inference time.
- ENet is the best architecture in terms of parameters space utilisation
No comments:
Post a Comment